2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사
변형 문제 4

일반 워크북 형태의 문제에서 벗어나 The Makings가 만든
2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 4
출판사에서 오랫동안 영어 번역과 교정을 하셨던 원어민 선생님과
현직에서 강사를 하고 있는 연구진들이 학생들을 위한 최상의
2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 4 를 선보입니다.
사고력과 이해력을 요구하는 문제들로 내신 대비 뿐만이 아니라
수능도 한꺼번에 공부하실 수 있는 자료입니다.
중간고사&기말고사 전에 더메이킹스(The Makings)에서 제작한
2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제로 마무리 하세요.
정답 확인하러가기!
https://themakings.co.kr/81/?idx=637
themakings.co.kr
The Makings의 2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제는
총 11개의 유형으로 구성되어 있습니다.
1. 빈칸 채우기(객관식)
2. 글의 내용 일치/불일치(객관식/한글 선택지)
3. 글의 내용 일치/불일치(객관식/영어 선택지)
4. 글 끼어 넣기(객관식)
5. 어법(서술형)
6. 어휘(서술형)
7. 주제문(객관식/영어 선택지)
8. 어휘 빈칸 채우기(서술형)
9. 영작(서술형)
10. 요약문 완성하기(서술형)
11. 문단 재배열 하기(객관식)
더메이킹스(The Makings)가 제작한 2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사
변형 문제 4의 지문입니다.
1번 지문(문항 번호 37번)
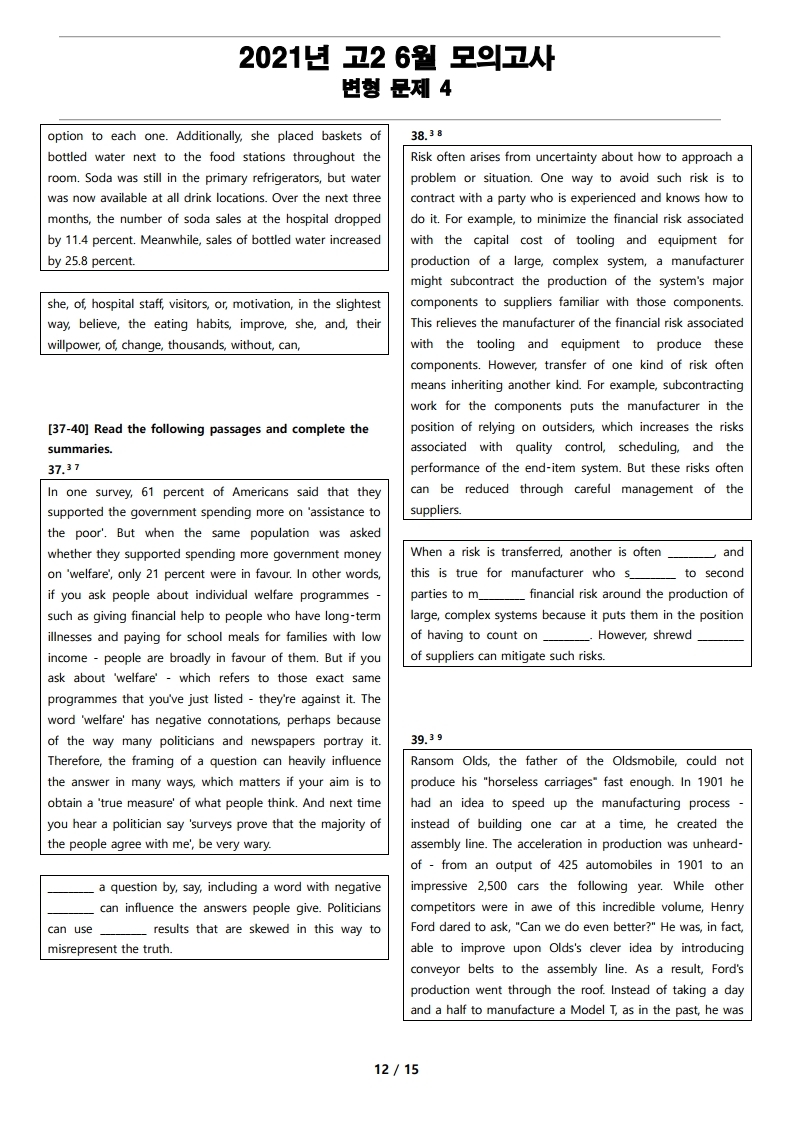
In one survey, 61 percent of Americans said that they supported the government spending more on 'assistance to the poor'. But when the same population was asked whether they supported spending more government money on 'welfare', only 21 percent were in favour. In other words, if you ask people about individual welfare programmes - such as giving financial help to people who have long‑term illnesses and paying for school meals for families with low income - people are broadly in favour of them. But if you ask about 'welfare' - which refers to those exact same programmes that you've just listed - they're against it. The word 'welfare' has negative connotations, perhaps because of the way many politicians and newspapers portray it. Therefore, the framing of a question can heavily influence the answer in many ways, which matters if your aim is to obtain a 'true measure' of what people think. And next time you hear a politician say 'surveys prove that the majority of the people agree with me', be very wary.
2번 지문(문항 번호 38번)
Risk often arises from uncertainty about how to approach a problem or situation. One way to avoid such risk is to contract with a party who is experienced and knows how to do it. For example, to minimize the financial risk associated with the capital cost of tooling and equipment for production of a large, complex system, a manufacturer might subcontract the production of the system's major components to suppliers familiar with those components. This relieves the manufacturer of the financial risk associated with the tooling and equipment to produce these components. However, transfer of one kind of risk often means inheriting another kind. For example, subcontracting work for the components puts the manufacturer in the position of relying on outsiders, which increases the risks associated with quality control, scheduling, and the performance of the end‑item system. But these risks often can be reduced through careful management of the suppliers.
3번 지문(문항 번호 39번)
Ransom Olds, the father of the Oldsmobile, could not produce his "horseless carriages" fast enough. In 1901 he had an idea to speed up the manufacturing process - instead of building one car at a time, he created the assembly line. The acceleration in production was unheard‑of - from an output of 425 automobiles in 1901 to an impressive 2,500 cars the following year. While other competitors were in awe of this incredible volume, Henry Ford dared to ask, "Can we do even better?" He was, in fact, able to improve upon Olds's clever idea by introducing conveyor belts to the assembly line. As a result, Ford's production went through the roof. Instead of taking a day and a half to manufacture a Model T, as in the past, he was now able to spit them out at a rate of one car every ninety minutes. The moral of the story is that good progress is often the herald of great progress.
4번 지문(문항 번호 40번)
Anne Thorndike, a primary care physician in Boston, had a crazy idea. She believed she could improve the eating habits of thousands of hospital staff and visitors without changing their willpower or motivation in the slightest way. In fact, she didn't plan on talking to them at all. Thorndike designed a study to alter the "choice architecture" of the hospital cafeteria. She started by changing how drinks were arranged in the room. Originally, the refrigerators located next to the cash registers in the cafeteria were filled with only soda. She added water as an option to each one. Additionally, she placed baskets of bottled water next to the food stations throughout the room. Soda was still in the primary refrigerators, but water was now available at all drink locations. Over the next three months, the number of soda sales at the hospital dropped by 11.4 percent. Meanwhile, sales of bottled water increased by 25.8 percent.
'전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 > 고2 모의고사 변형 문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2021년 고2 9월 전국 연합 모의고사(인천시)변형 문제 2 (0) | 2021.09.11 |
|---|---|
| 2021년 고2 9월 전국 연합 모의고사(인천시)변형 문제 1 (0) | 2021.09.10 |
| 2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 3 (0) | 2021.06.15 |
| 2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 2 (0) | 2021.06.14 |
| 2021년 고2 6월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 1 (0) | 2021.06.13 |