2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사
변형 문제 3
일반 워크북 형태의 문제에서 벗어나 The Makings가 만든
2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 3
출판사에서 오랫동안 영어 번역과 교정을 하셨던 원어민 선생님과
현직에서 강사를 하고 있는 연구진들이 학생들을 위한 최상의
2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 3 을 선보입니다.
사고력과 이해력을 요구하는 문제들로 내신 대비 뿐만이 아니라
수능도 한꺼번에 공부하실 수 있는 자료입니다.
중간고사&기말고사 전에 더메이킹스(The Makings)에서 제작한
2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제로 마무리 하세요.
정답 확인하러가기!
http://themakings.co.kr/70/?idx=528
2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제
2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제, 내신대비, 영어내신자료,고등영어자료, 모의고사 변형문제,전국 연합모의고사 변형자료, 모의고사 영어 서술형 대비, 대치동 고등 영어자료, 대치
themakings.co.kr
themakings.co.kr

The Makings의 2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사
변형 문제는 총 11개의 유형으로 구성되어 있습니다.
1. 빈칸 채우기(객관식)
2. 글의 내용 일치/불일치(객관식/한글 선택지)
3. 글의 내용 일치/불일치(객관식/영어 선택지)
4. 글 끼어 넣기(객관식)
5. 어법(서술형)
6. 어휘(서술형)
7. 주제문(객관식/영어 선택지)
8. 어휘 빈칸 채우기(서술형)
9. 영작(서술형)
10. 요약문 완성하기(서술형)
11. 문단 재배열 하기(객관식)
더메이킹스(The Makings)가 제작한
2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 3의 지문입니다.
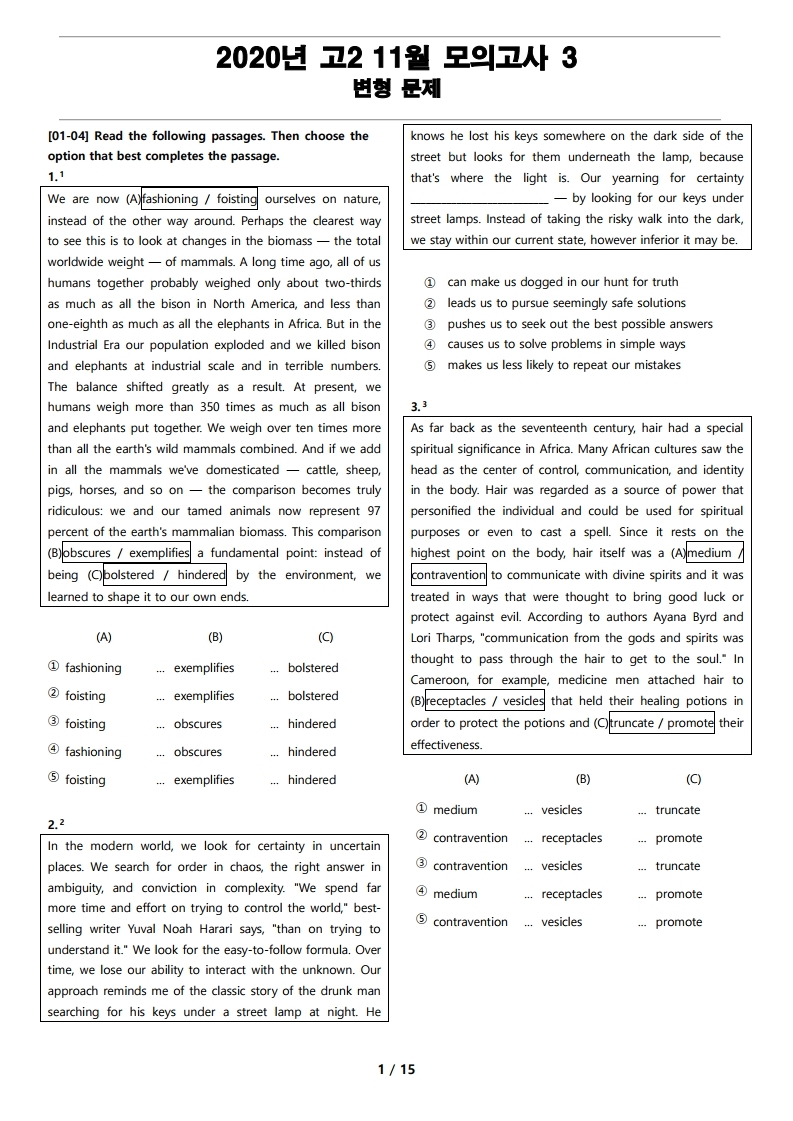
1번 지문(문항 번호 33번)
We are now imposing ourselves on nature, instead of the other way around. Perhaps the clearest way to see this is to look at changes in the biomass — the total worldwide weight — of mammals. A long time ago, all of us humans together probably weighed only about two-thirds as much as all the bison in North America, and less than one-eighth as much as all the elephants in Africa. But in the Industrial Era our population exploded and we killed bison and elephants at industrial scale and in terrible numbers. The balance shifted greatly as a result. At present, we humans weigh more than 350 times as much as all bison and elephants put together. We weigh over ten times more than all the earth's wild mammals combined. And if we add in all the mammals we've domesticated — cattle, sheep, pigs, horses, and so on — the comparison becomes truly ridiculous: we and our tamed animals now represent 97 percent of the earth's mammalian biomass. This comparison illustrates a fundamental point: instead of being limited by the environment, we learned to shape it to our own ends.
2번 지문(문항 번호 34번)
In the modern world, we look for certainty in uncertain places. We search for order in chaos, the right answer in ambiguity, and conviction in complexity. "We spend far more time and effort on trying to control the world," best-selling writer Yuval Noah Harari says, "than on trying to understand it." We look for the easy-to-follow formula. Over time, we lose our ability to interact with the unknown. Our approach reminds me of the classic story of the drunk man searching for his keys under a street lamp at night. He knows he lost his keys somewhere on the dark side of the street but looks for them underneath the lamp, because that's where the light is. Our yearning for certainty leads us to pursue seemingly safe solutions — by looking for our keys under street lamps. Instead of taking the risky walk into the dark, we stay within our current state, however inferior it may be.
3번 지문(문항 번호 35번)
As far back as the seventeenth century, hair had a special spiritual significance in Africa. Many African cultures saw the head as the center of control, communication, and identity in the body. Hair was regarded as a source of power that personified the individual and could be used for spiritual purposes or even to cast a spell. Since it rests on the highest point on the body, hair itself was a means to communicate with divine spirits and it was treated in ways that were thought to bring good luck or protect against evil. According to authors Ayana Byrd and Lori Tharps, "communication from the gods and spirits was thought to pass through the hair to get to the soul." In Cameroon, for example, medicine men attached hair to containers that held their healing potions in order to protect the potions and enhance their effectiveness.
4번 지문(문항 번호 36번)
Mark Granovetter examined the extent to which information about jobs flowed through weak versus strong ties among a group of people. He found that only a sixth of jobs that came via the network were from strong ties, with the rest coming via medium or weak ties; and with more than a quarter coming via weak ties. Strong ties can be more homophilistic. Our closest friends are often those who are most like us. This means that they might have information that is most relevant to us, but it also means that it is information to which we may already be exposed. In contrast, our weaker relationships are often with people who are more distant both geographically and demographically. Their information is more novel. Even though we talk to these people less frequently, we have so many weak ties that they end up being a sizable source of information, especially of information to which we don't otherwise have access.
'전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 > 고2 모의고사 변형 문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2021년 고2 3월 전국연합모의고사 변형문제 (0) | 2021.04.09 |
|---|---|
| 2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 영어 변형 문제 4 (0) | 2020.12.04 |
| 2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 2 (0) | 2020.12.01 |
| 2020년 고2 11월 전국 연합 모의고사 영어 변형 문제 01 (0) | 2020.11.25 |
| 2020년 고2 9월 전국 연합 모의고사 변형 문제 4 (0) | 2020.09.30 |